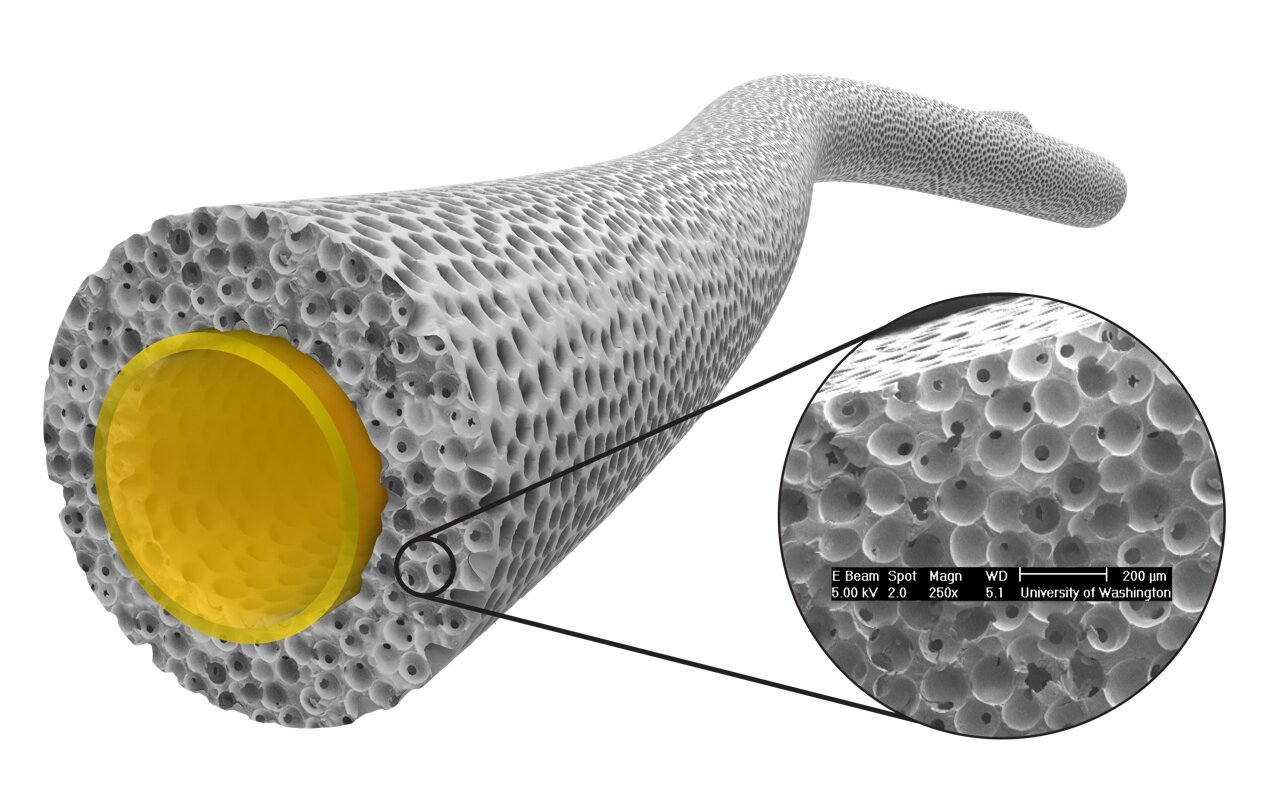
Vascular grafts are an integral component of modern cardiovascular medicine, playing a pivotal role in a variety of procedures aimed at restoring blood flow, treating blocked arteries, and repairing weakened blood vessels. The vascular graft market is expanding rapidly, driven by technological innovations, the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and advancements in medical materials. As cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death worldwide, the importance of effective vascular grafts has never been greater.
Understanding Vascular Grafts and Their Importance
A vascular graft is a surgical implant designed to replace or bypass blocked or damaged blood vessels. These devices have become an essential tool in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary artery disease, aneurysms, and end-stage renal disease. Vascular grafts are particularly crucial in coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, where they are used to bypass blocked coronary arteries and restore normal blood flow to the heart muscle. This procedure is often performed in patients suffering from severe coronary artery disease, a condition that can result in heart failure or even death if untreated.
Additionally, vascular grafts play a crucial role in dialysis for individuals with kidney failure. In hemodialysis, these grafts allow for easy access to the bloodstream, facilitating the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the body. Moreover, vascular grafts are used to repair aneurysms, which occur when blood vessels weaken and bulge, posing a significant risk of rupture.
Types of Vascular Grafts
There are several types of vascular grafts used in modern medical practice. Each type is designed to address specific patient needs and medical conditions. The most commonly used types include:
- Synthetic Vascular Grafts: These are made from synthetic materials such as ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene) and polyester. Synthetic grafts are popular due to their durability, resistance to infection, and ability to provide long-term vascular support. They are often used in coronary bypass surgeries and dialysis access procedures.
- Biological Vascular Grafts: Derived from animal tissues, such as bovine pericardium or porcine small intestine submucosa, biological grafts are more biologically compatible, offering better integration with the patient’s tissues. They are often used in younger patients who are at risk of rejection from synthetic grafts.
- Composite Vascular Grafts: These combine both synthetic and biological materials to offer the benefits of both types. They are often used for more complex medical conditions where a combination of materials is required to ensure better functionality and durability.
The Growth of the Vascular Graft Market
The vascular graft market is experiencing robust growth, primarily due to the increasing incidence of cardiovascular diseases and the aging global population. As life expectancy increases, the prevalence of age-related cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary artery disease and aortic aneurysms, is rising. This has led to a growing demand for vascular grafts, which are considered essential in the treatment of these conditions.
Technological advancements are also fueling market expansion. The development of advanced materials such as biocompatible coatings and antimicrobial grafts has improved the longevity and effectiveness of grafts. Additionally, minimally invasive techniques, including endovascular procedures, are reducing recovery times and enhancing the overall patient experience.
The global market for vascular grafts is also benefiting from increasing healthcare spending and greater awareness of cardiovascular diseases. Regions like North America and Europe are at the forefront of this market, thanks to well-established healthcare infrastructure and high rates of cardiovascular disease. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid growth, driven by improving healthcare access and rising cardiovascular disease rates.
Challenges and Barriers in the Market
Despite the growing demand for vascular grafts, the market faces several challenges. High treatment costs remain one of the primary obstacles, especially in developing regions where healthcare budgets are limited. Moreover, surgical complications, such as graft infection, thrombosis, and graft failure, can pose significant challenges, necessitating follow-up procedures or even further surgeries.
Supply chain issues related to sourcing biological graft materials and the lack of skilled professionals in underserved regions also present barriers to market growth. These challenges are compounded by regulatory hurdles, as the approval process for new vascular graft technologies can be time-consuming and expensive.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of vascular grafts looks promising, with advancements in 3D printing and tissue engineering likely to transform the field. 3D-printed grafts offer personalized solutions tailored to a patient’s specific vascular anatomy, reducing the risk of complications. Additionally, bioengineered grafts created from a patient’s own cells could eliminate issues related to graft rejection and improve long-term outcomes.
Nanotechnology is another area of significant potential. Researchers are exploring how nanomaterials can be used to create grafts with enhanced durability and antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of infection and improving the integration of grafts with the body.
Conclusion
Vascular grafts are a critical component in the management of cardiovascular diseases and other vascular conditions. With advancements in technology and an increasing focus on improving patient outcomes, the vascular graft market is poised for continued growth. While challenges remain, ongoing research and innovation are paving the way for more effective and accessible treatments. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, vascular grafts will remain a cornerstone of cardiovascular care, offering patients a chance for better quality of life and improved health outcomes.