The healthcare industry continuously seeks innovative ways to improve patient outcomes, and non-invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation (nVNS) is at the forefront of these efforts. This groundbreaking technology eliminates the need for surgery, making it a safer, more accessible treatment option for various medical conditions.
Understanding Non-Invasive VNS
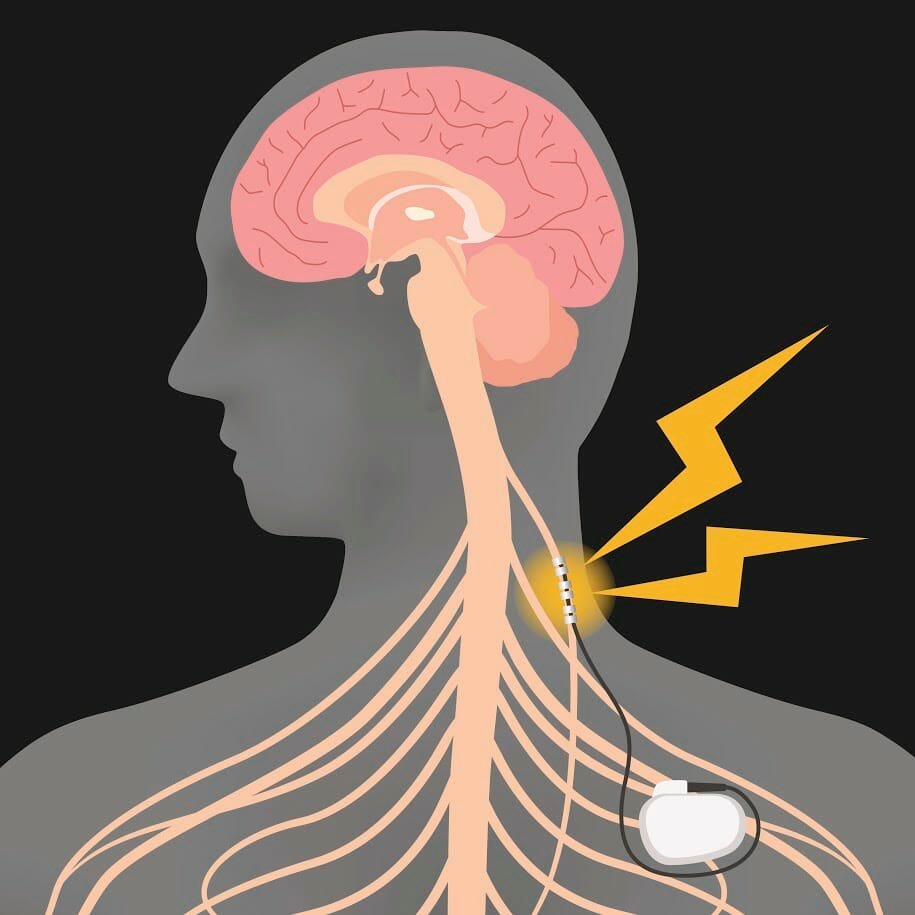
Traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation involves implanting a device surgically to deliver electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. In contrast, nVNS achieves the same therapeutic effect using external devices applied to the neck or ear, targeting the nerve through the skin.
Why Choose nVNS?
- Eliminating Surgical Risks:
One of the most significant benefits of nVNS is its non-invasive nature. Traditional VNS requires surgical implantation, posing risks like infection, scarring, and recovery time. nVNS eliminates these risks, providing a safer alternative. - Enhanced Accessibility:
nVNS devices are portable and user-friendly, allowing patients to use them at home. This accessibility empowers individuals to take control of their treatment, reducing dependency on healthcare facilities. - Cost Efficiency:
Without the need for surgery, nVNS significantly lowers treatment costs, making it a viable option for patients in low-resource settings. - Broader Acceptance:
The simplicity of nVNS makes it more acceptable to patients who may be hesitant about invasive procedures, increasing its adoption in clinical practice.
Clinical Applications of nVNS
Non-invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation is a versatile therapy, finding applications in various medical conditions:
- Migraines: nVNS devices have shown effectiveness in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
- Epilepsy: Like traditional VNS, nVNS helps control seizures in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, offering a non-surgical alternative.
- Mental Health Disorders: Emerging research supports the use of nVNS for anxiety, PTSD, and even depression, expanding its scope in mental health treatment.
- Chronic Pain: Studies suggest nVNS can be beneficial in managing chronic pain conditions, providing relief where traditional methods fail.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, nVNS faces some challenges:
- Limited Awareness: Many patients and healthcare providers are unaware of nVNS and its potential benefits, limiting its adoption.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining approval from regulatory bodies can delay the introduction of new devices into the market.
- Initial Costs: While nVNS reduces long-term costs, the upfront cost of devices may still be a barrier for some patients.
The Future of nVNS
The future of non-invasive VNS is promising, with technological advancements driving its evolution. Wearable devices integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) are on the horizon, offering personalized treatment plans based on patient data. These innovations will further simplify the use of nVNS and enhance its effectiveness.
Healthcare providers and device manufacturers are also collaborating to increase awareness and accessibility. Educational campaigns, coupled with clinical research, aim to highlight the benefits of nVNS, fostering its adoption in mainstream healthcare.
Conclusion
Non-invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation is more than a therapy—it’s a beacon of hope for patients seeking effective, patient-friendly treatments. As technology advances and awareness grows, nVNS is set to transform healthcare, making life better for millions worldwide.